The importance of saving endangered species for a sustainable future
Endangered species are plant or animal species at risk of becoming extinct due to various factors such as habitat loss, changing environmental conditions, poaching, and pollution. Protecting endangered species is vital as they play a significant role in maintaining ecosystem balance and diversity. For instance, some help with pollination and seed dispersal, while others regulate the population of other organisms in the food chain. Unfortunately, the current number of endangered species is alarming, with many species facing the threat of extinction. Therefore, it's essential to take action to protect them and prevent their disappearance from our planet.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(1).png)
Baby Sumatran elephant.
What are endangered species?
Endangered species are living organisms whose population sizes have declined to critical levels, putting them at risk of extinction. These species are categorised as endangered when their populations have decreased to such a degree that they are likely to disappear entirely from their natural habitats if appropriate conservation measures are not implemented.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is responsible for classifying species as endangered or critically endangered based on criteria such as population size, habitat loss, and geographic range. The loss of endangered species can significantly impact the ecosystem, as they play vital roles in maintaining ecological balance.
The importance of protecting endangered species
Endangered species play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of our planet. They provide essential ecosystem services such as pollination, seed dispersal, and regulating the population of other organisms in the food chain. They also have important medicinal, cultural, and aesthetic values.
Read more: Why should endangered species be protected?
Protecting endangered species is therefore crucial in ensuring these services are preserved for future generations. Additionally, conservation efforts protecting endangered species can lead to the conservation of other species and their habitats, ultimately contributing to the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(4).png) Black rhinoceros.
Black rhinoceros.
An overview of the current state of endangered species
The current state of endangered species is alarming, with many species facing the threat of extinction. According to the IUCN, over 42,000 species are threatened with extinction, representing around 28% of all assessed species. Threats to endangered species come from various factors, including habitat loss, changing environmental conditions, pollution, overexploitation, and invasive species.
Some iconic species currently at risk of extinction include the Sumatran orangutan, the Asian and African forest elephant, the black rhino, and the vaquita porpoise. To address the challenge of protecting endangered species, conservation efforts such as habitat restoration, captive breeding programmes, and wildlife trafficking enforcement are essential.
Do you wish to contribute to making the world a better place? Start with planting a tree today.
What are the causes of endangerment?
Habitat loss and fragmentation
Habitat loss and fragmentation are major drivers of species endangerment. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanisation, and land conversion for agriculture result in the loss and fragmentation of natural habitats. It leads to the displacement of species from their native habitats, reducing their ability to access resources and breeding sites and increasing their vulnerability to predation and other threats. Efforts to protect endangered species must, therefore, involve habitat restoration and the preservation of natural habitats to ensure species can thrive in their natural environments.
Read more: The importance of forests in bumble bee conservation
Environmental instability
Environmental instability poses significant threats to many species, particularly those in vulnerable habitats such as polar regions and coral reefs. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt the distribution and abundance of many species. For example, rising sea levels caused by melting glaciers and ice caps threaten polar bears' survival, while coral bleaching events are causing the loss of coral reef ecosystems. Reducing carbon emissions is therefore critical for protecting endangered species.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(5).png)
Polar bear sitting on the edge of an ice floe in the Svalbard Archipelago.
Hunting and poaching
Hunting and poaching are also major contributors to species endangerment. These activities are driven by the demand for animal products such as ivory, fur, and meat. They also often target species already at risk of extinction. Poaching threatens the survival of species vital to maintaining ecosystem balance, such as apex predators. To protect endangered species from hunting and poaching, law enforcement measures must be strengthened, and demand for illegal animal products must be reduced through public awareness campaigns.
Read more: Africa’s elephants are two different species, and both are endangered
Pollution
Pollution from various sources, such as industrial activities, agriculture, and urbanisation, poses a significant threat to many species. Chemical pollutants such as pesticides and heavy metals can accumulate in the food chain, leading to chronic health problems and reduced reproductive success. Pollution can also alter the chemistry and physical properties of water bodies, leading to the death of aquatic species. To mitigate the impacts of pollution on endangered species, strict regulations must be implemented to limit the release of pollutants into the environment, along with the adoption of sustainable practices.
Invasive species
Invasive species are non-native species introduced to an ecosystem and capable of outcompeting native species. They can displace and disrupt the ecological roles of native species, leading to their decline and eventual extinction. Invasive species can also introduce diseases and parasites to native populations, further increasing their vulnerability. To protect endangered species from invasive ones, measures such as early detection, rapid response, and quarantine regulations for high-risk species are necessary.
Integrate trees into your business
We can help your company become more sustainable by integrating trees into your business.
Examples of endangered species
A brief overview of some of the most endangered species in the world
From charismatic mammals to lesser-known invertebrates, a wide range of species are at risk of extinction due to various human-driven threats. The Sumatran orangutan, for instance, is a critically endangered great ape species found only on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia. Its population has declined rapidly due to habitat loss and poaching, with estimates indicating that only around 14,000 individuals remain in the wild.
Read more: Silverback gorilla—endangered species or not?
Similarly, the vaquita porpoise, found only in the Gulf of California, Mexico, is the world's most endangered marine mammal, with fewer than 10 individuals remaining.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(3).png)
Beached porpoise rescued on the Dutch island Texel.
The black rhinoceros, native to Africa, is another iconic species heavily targeted by poachers for its horn, leading to a significant population decline. Other endangered species include the Javan rhinoceros, Asian and African forest elephant, and Hawksbill sea turtle, among many others.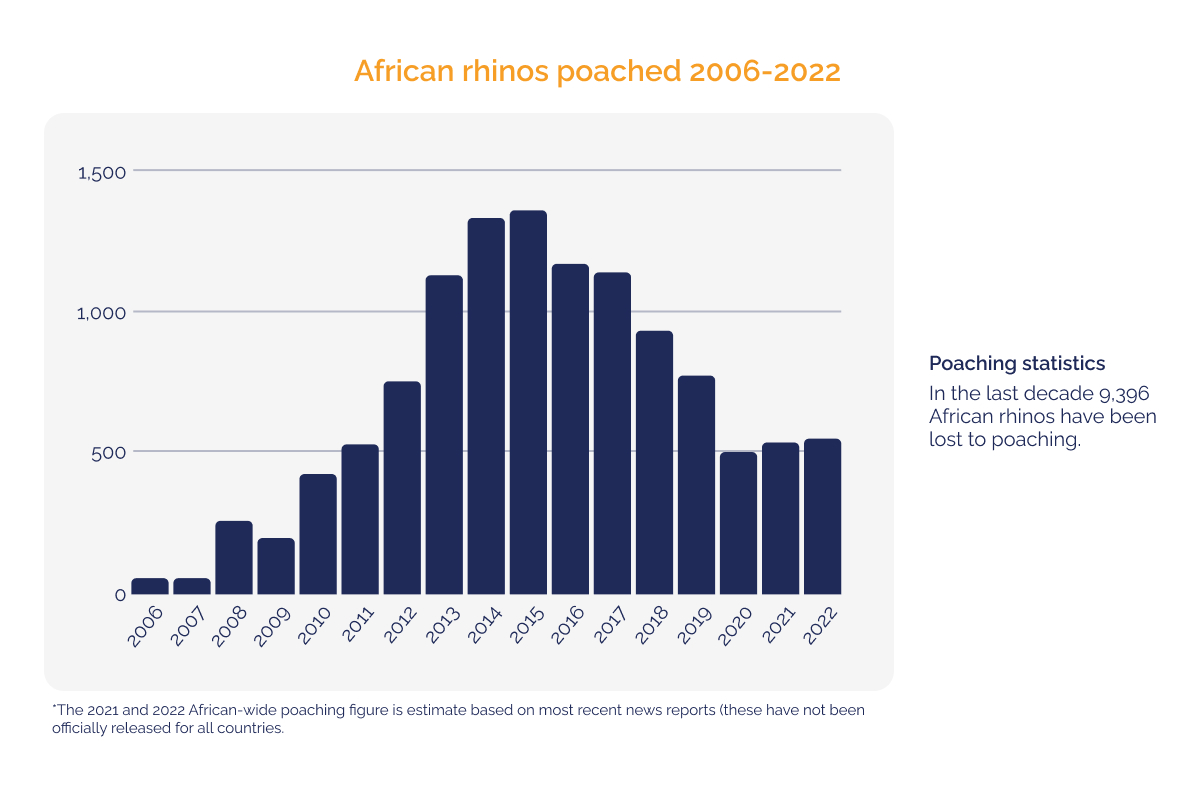
Source: https://www.savetherhino.org/rhino-info/poaching-stats
What makes these species unique and important?
These endangered species are unique and important due to their ecological and cultural value. For instance, orangutans play a crucial role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration, while rhinoceroses and elephants are keystone species, playing a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitats.
Many of these species also have cultural and economic significance, with tourism and ecotourism contributing to local economies in many regions. Furthermore, the loss of these species can have significant cascading effects, leading to the decline of other species and the degradation of entire ecosystems. Protecting these species is, therefore, not only essential for their own survival but also for the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning as a whole.
Make a difference: Calculate your carbon footprint
Conservation efforts
An overview of conservation efforts around the world
An overview of conservation efforts around the world shows that many organisations and governments are working towards protecting endangered species and their habitats. These efforts range from habitat restoration and species reintroduction to law enforcement and community engagement programmes. For instance, the IUCN developed a global strategy for conserving threatened species and their habitats, while the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) regulates international trade in endangered species. Many countries have also established protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, to safeguard species and their habitats.
Read more about DGB's habitat restoration efforts in Uganda
Examples of successful conservation efforts and their impact
The recovery of the southern white rhinoceros, which was on the brink of extinction in the early 20th century, is a notable example of successful conservation efforts. Conservation efforts, including captive breeding and translocation programmes, have helped increase the population from fewer than 100 individuals to over 18,000 today.
Another example is the recovery of the bald eagle in North America, which was brought back from the brink of extinction through habitat protection and the banning of the pesticide DDT. The conservation efforts not only led to the recovery of these species but also contributed to restoring ecosystems and preserving cultural and economic values.
Read more: From the brink of extinction: four endangered species that made a comeback
Challenges in conservation and what more can be done
Conservation efforts face several challenges. These include habitat loss, environmental instability, invasive species, and political and social factors such as poverty and conflict. Additionally, conservation efforts can be hampered by limited funding and inadequate resources, as well as a lack of public awareness and support.
To address these challenges, it is essential to increase funding and resources for conservation efforts, develop effective policies and regulations, and engage with local communities and stakeholders. Collaboration between governments, conservation organisations, and local communities is also critical for the success of conservation efforts. Furthermore, new technologies and innovative approaches, such as genetic engineering and citizen science, can be leveraged to enhance conservation efforts.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(2).png)
Mount Kilimanjaro and a herd of elephants, Amboseli National Park.
The role of individuals in saving endangered species
How can individuals help protect endangered species
Individuals can play a significant role in protecting endangered species and their habitats through various actions. These actions include reducing their carbon footprint, consuming sustainable products, supporting conservation organisations, and advocating for conservation policies. Individuals can also influence social norms and promote sustainable behaviours in their communities, creating a ripple effect that can significantly impact conservation efforts.
Calculate your carbon footprint to start making a difference
Actions individuals can take to make a difference
There are numerous actions individuals can take to make a difference. One way individuals can contribute to conservation efforts is by supporting organisations that work towards protecting endangered species and their habitats. This can include making donations, volunteering, or participating in awareness-raising campaigns.
Another way individuals can help is by reducing their carbon footprint by adopting more sustainable practices such as using public transport, reducing meat consumption, and using energy-efficient appliances. Additionally, individuals can make a difference by avoiding products that contribute to habitat destruction, like palm oil, and supporting sustainable alternatives. Engaging in eco-tourism and promoting responsible tourism practices can also help support local communities and conservation efforts.
The role of individuals in saving endangered species is essential, and everyone can contribute to conservation efforts in their unique way. By taking action to reduce their environmental impact, supporting conservation organisations, and promoting sustainable practices, individuals can make a meaningful difference in protecting endangered species and preserving the planet's biodiversity.
Read more: 7 Strategies for protecting wildlife
Let us inform you
We will keep you updated on all the latest news.
A global commitment to saving endangered species
A summary of the importance of saving endangered species emphasises the critical role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems, supporting human livelihoods, and preserving cultural and spiritual values. Endangered species are a vital component of biodiversity and play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, such as pollination, pest control, and nutrient cycling. Their extinction can have far-reaching consequences, leading to ecosystem degradation, loss of cultural and economic values, and social conflicts.
All individuals, and society as a whole, need to take action to protect endangered species underscoring the urgent need for collective efforts to address the challenges facing biodiversity conservation. Protecting endangered species requires action at various levels, from individual actions to policy interventions and international collaborations. Individuals can take action by making sustainable choices, supporting conservation organisations, and advocating for policies that protect biodiversity. At the same time, governments and international organisations need to invest in conservation efforts, develop effective policies and regulations, and engage with local communities to ensure sustainable and equitable conservation outcomes.
In conclusion, protecting endangered species is crucial for ensuring a healthy and sustainable planet for present and future generations. Saving endangered species requires collective efforts and action from individuals, governments, and society as a whole.
Our projects
We develop large-scale, impactful projects.
DGB Group’s commitment to saving endangered species
At DGB Group, we are dedicated to restoring natural habitats and giving nature back its power. This is our long-term vision that we get closer to every single day. We have the power to make a difference, and by working together, we can ensure that endangered species are protected and biodiversity is conserved for generations to come.
Our Uganga reforestation project is especially significant in safeguarding endangered species. That is because the area of our project is home to the Bulindi chimpanzees. Research in 2021 highlighted that 80% of their habitat was lost due to deforestation. Our project is designed to plant at least one million trees every year for the coming three years. For this purpose, indigenous trees were specifically picked by our ecologists to ensure the reconstruction of the chimpanzees’ habitat. This is just one instance of how our tree-planting projects support the conservation of various species.
Join us in helping nature prosper and flourish

.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(1).png)
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(4).png)
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(5).png)
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(3).png)

.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Saving%20Endangered%20Species%20(2).png)
