In a world where environmental concerns are rising, the search for innovative ways to effectively store carbon emissions takes centre stage. Among the unique solutions capturing attention, one shines brightly: biochar. In this blog post, we invite you to journey into the realm of biochar, a captivating substance with the power to revolutionise soil, plants, food security, sustainability, and even the economy. Explore the fascinating process of biochar production, uncover its diverse applications, and discover its extraordinary effects on our natural world.

What is biochar, and how is it made?
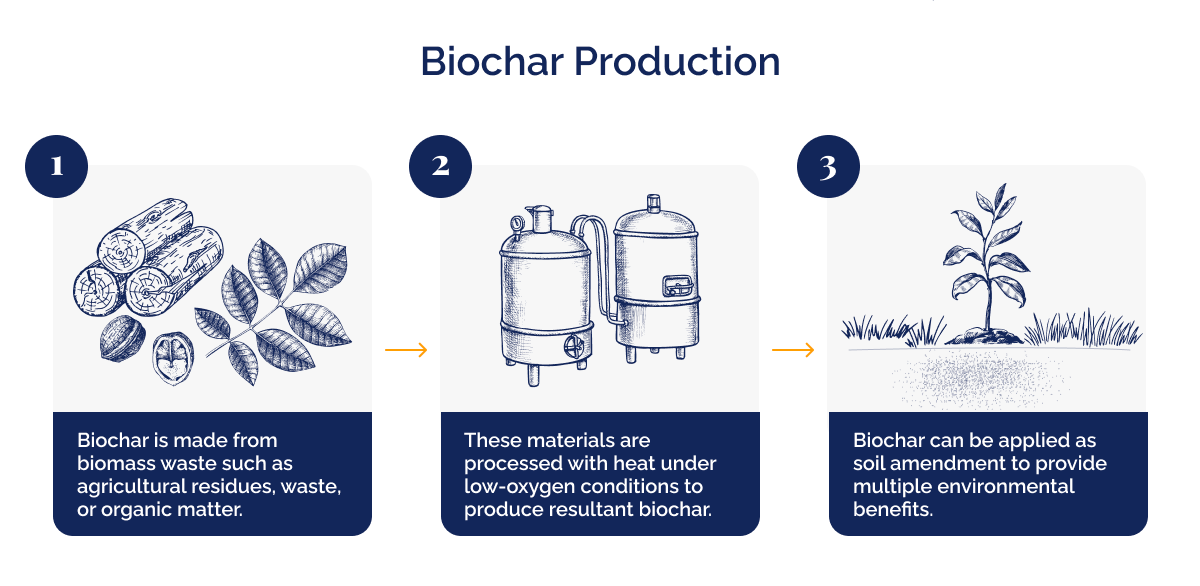
Biochar is a highly porous, carbon-rich material that is produced through the process of pyrolysis. Pyrolysis involves heating biomass, such as agricultural waste or wood, in the absence of oxygen. This process transforms the biomass into a stable form of carbon that can be stored in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years.
Biochar production starts with the collection of biomass, which can include materials like crop residues, wood chips, sawdust, or even animal manure. These biomass sources are chosen based on their availability and suitability for the pyrolysis process. Once the biomass is collected, it is dried to reduce moisture content and then processed into smaller pieces.
The pyrolysis process takes place in a specially-designed reactor or kiln. The biomass is heated to high temperatures, typically between 400 to 700 degrees Celsius, in an oxygen-limited environment. The absence of oxygen prevents the biomass from burning and initiates the breakdown of organic matter through a complex chemical reaction.
During pyrolysis, the biomass undergoes several stages. First, volatile compounds are released as gases, which can be collected and used as a source of renewable energy. These gases can be used to generate heat or electricity, providing an additional benefit to the biochar production process. As the temperature increases, the remaining solid material undergoes further decomposition and carbonisation, ultimately forming biochar.
Read more: Turning waste into opportunity: The feasibility stage of our biochar project
Once the pyrolysis process is complete, the biochar is cooled and then crushed into smaller particles. The resulting biochar is a stable and carbon-rich material that can be directly applied to the soil or further processed for specific applications.
 The process of biochar production
The process of biochar production
What is biochar used for?
Biochar's most remarkable attribute is its exceptional carbon storage capacity. It has the potential to sequester substantial amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By storing carbon in the soil, biochar helps to offset greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions.
Beyond carbon storage, biochar has numerous applications across various industries:
- Agriculture: Biochar is widely used in agriculture as a soil amendment. When applied to the soil, biochar improves soil fertility by enhancing nutrient retention, reducing nutrient leaching, and promoting healthier root systems. It also increases water holding capacity, reducing irrigation needs and improving plant drought resistance.
- Environmental remediation: Biochar has shown promise in environmental remediation applications. It can effectively capture and remove contaminants from soil and water, acting as a natural filter. Its porous structure allows it to absorb heavy metals, organic pollutants, and even certain pesticides, helping to improve soil and water quality.
- Waste management: Biochar offers a sustainable solution for managing organic waste. By diverting biomass materials, such as agricultural residues or forestry byproducts, from traditional waste disposal methods, biochar production helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and prevents the release of harmful substances into the environment.
- Livestock and manure management: Biochar can be used to improve livestock and manure management practices. When added to animal bedding or incorporated into manure storage systems, biochar helps reduce odours, control pathogens, and promote nutrient retention, contributing to more sustainable and environmentally friendly livestock operations.
- Renewable energy: While biochar production generates renewable energy by utilising gases released during pyrolysis, biochar can also be used as a biomass fuel source. It can be co-fired (the combustion of two different fuels in the same combustion system) with other fuels to generate heat or electricity, providing a renewable energy option that helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The diverse applications of biochar highlight its versatility and potential to address multiple environmental challenges while promoting sustainable practices across various industries.
 Dr Anubhav Mohiley stands in front of a pile of sugar cane biowaste.
Dr Anubhav Mohiley stands in front of a pile of sugar cane biowaste.
Biochar’s effect on soil and plants
Biochar has many positive effects on the environment. It is especially beneficial for soil and plants, offering the following benefits:
- Chemical effects: When biochar is applied to the soil, it interacts with various chemical components, enhancing soil fertility. It improves nutrient retention, reduces the leaching of essential elements, and balances soil pH levels. These chemical transformations create a more suitable environment for plant growth.
- Physical effects: Biochar also improves soil structure and water-holding capacity. Its porous nature allows for increased water and nutrient retention, reducing the need for irrigation and fertilisers. Additionally, it enhances soil aeration, promoting healthier root systems and overall plant growth.
- Microbial responses: Introducing biochar to the soil positively influences microbial activity. It enhances the abundance and diversity of beneficial microorganisms, leading to improved nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and increased plant resilience.
Biochar's role in food security, sustainability, and a sustainable economy
Biochar has the potential to revolutionise agriculture and contribute to global food security. Making agricultural soils more productive and fertile increases crop yields—helping to meet the growing food demand—and reduces the need for expanding agricultural land into sensitive ecosystems.
The incorporation of biochar can also contribute to sustainable land management practices. It offers a solution for managing agricultural waste and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from organic materials that would otherwise decompose and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Furthermore, biochar can be produced using various types of biomass, including waste materials, which help recycle and reduce waste.
Biochar further presents opportunities for economic growth and rural development. Its production can create jobs in biomass collection, pyrolysis facilities, and biochar distribution networks. Additionally, the increased agricultural productivity associated with biochar can bolster local economies and reduce dependence on external resources. It provides a sustainable approach to land management that can support long-term economic stability.
Biochar vs charcoal vs activated carbon: What are the differences?
Biochar, charcoal, and activated carbon are all carbon-rich materials, but they differ in their production methods and applications.
- Biochar: Biochar is produced through the pyrolysis of biomass, such as agricultural waste or wood, in the absence of oxygen. This process converts the biomass into a stable form of carbon that can be used for carbon sequestration and soil enhancement. Biochar is primarily utilised for its ability to capture carbon, improve soil fertility, retain water, and cycle nutrients. It acts as a long-term carbon sink, helping to mitigate climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil for extended periods.
- Charcoal: Charcoal, on the other hand, is produced by heating wood in the presence of oxygen. This process, known as carbonisation, removes volatile compounds and moisture, leaving behind a carbon-rich residue. Charcoal is commonly used as a fuel source for heating and cooking purposes due to its high carbon content and long-lasting burn. It is often associated with barbecues and traditional cooking methods, where its high-heat-retention properties make it ideal for grilling.
- Activated carbon: Activated carbon undergoes further processing to increase its surface area and adsorption capacity. It is produced by heating carbonaceous materials, such as wood, coal, or coconut shells, at high temperatures and activating them with gases or chemicals. This activation process creates a highly porous structure with a large internal surface area. Activated carbon is widely used for its adsorption properties, which make it effective in filtering and purifying air, water, and other substances. It finds applications in various industries, including water treatment, air filtration, and gas purification.
The main differences between biochar, charcoal, and activated carbon lie in their production methods, physical properties, and intended applications. While biochar focuses on carbon sequestration and soil enhancement, charcoal is primarily used as a fuel source for heating and cooking. Activated carbon, with its highly porous structure, excels in adsorption and purification applications, serving as an effective filtration medium. Understanding the distinctions between these carbon-rich materials allows us to appreciate their unique roles and potential contributions in various fields and industries.
The promise of biochar in nature-based solutions
Biochar holds tremendous potential as an innovative carbon storage solution. Its ability to sequester carbon, improve soil fertility, and contribute to food security and sustainability make it a valuable tool in our fight against climate change and biodiversity loss. To maximise biochar’s benefits, further research and development are necessary to optimise its production techniques and explore its applications in diverse sectors.
 Dr Anubhav Mohiley examines the quality of bagasse.
Dr Anubhav Mohiley examines the quality of bagasse.
At DGB Group, we champion the strength of nature-based solutions and are committed to safeguarding and rejuvenating our precious natural environment through reforestation, afforestation, biodiversity restoration, and the revitalisation of degraded lands. Our comprehensive array of solutions allows businesses, investors, and individuals to actively partake in preserving nature in a direct and transparent manner. Together, let us forge a harmonious alliance with nature, nurturing and preserving the beauty that surrounds us.
Incorporating biochar into our agricultural practices and land management strategies can pave the way for a more sustainable future. Let’s embrace this new carbon storage solution and work together to positively impact our planet and ensure a better tomorrow for generations to come. By harnessing the power of biochar, we can significantly contribute to mitigating climate change and biodiversity loss and creating a more sustainable and resilient world.
Contact our team to find out how you can support our initiatives




