Indonesia, home to the world's third-largest tropical forests, is facing a significant deforestation crisis that is damaging its environment and biodiversity.

Causes of deforestation in Indonesia
Deforestation is the permanent destruction of forests and trees to make land available for other uses, such as agriculture, mining, and urban development. According to data from the Ministry of Environment and Forestry, Indonesia lost over 6 million hectares of forest cover from 2000 to 2012. This deforestation has caused significant environmental problems such as soil erosion, flooding, loss of wildlife habitats, and changes to the local climate.
Read more: Top 10 causes of deforestation
The primary cause of deforestation in Indonesia is the expansion of agriculture. Indonesia is the world's largest palm oil producer, and the industry has rapidly expanded, leading to extensive land clearing for palm oil plantations. The logging industry is also a significant contributor to deforestation, with illegal logging occurring in many protected areas. Additionally, mining activities, such as coal and gold mining, have led to the destruction of large areas of forests and the pollution of waterways.
Read more: Deforestation in Asia: a call for conservation
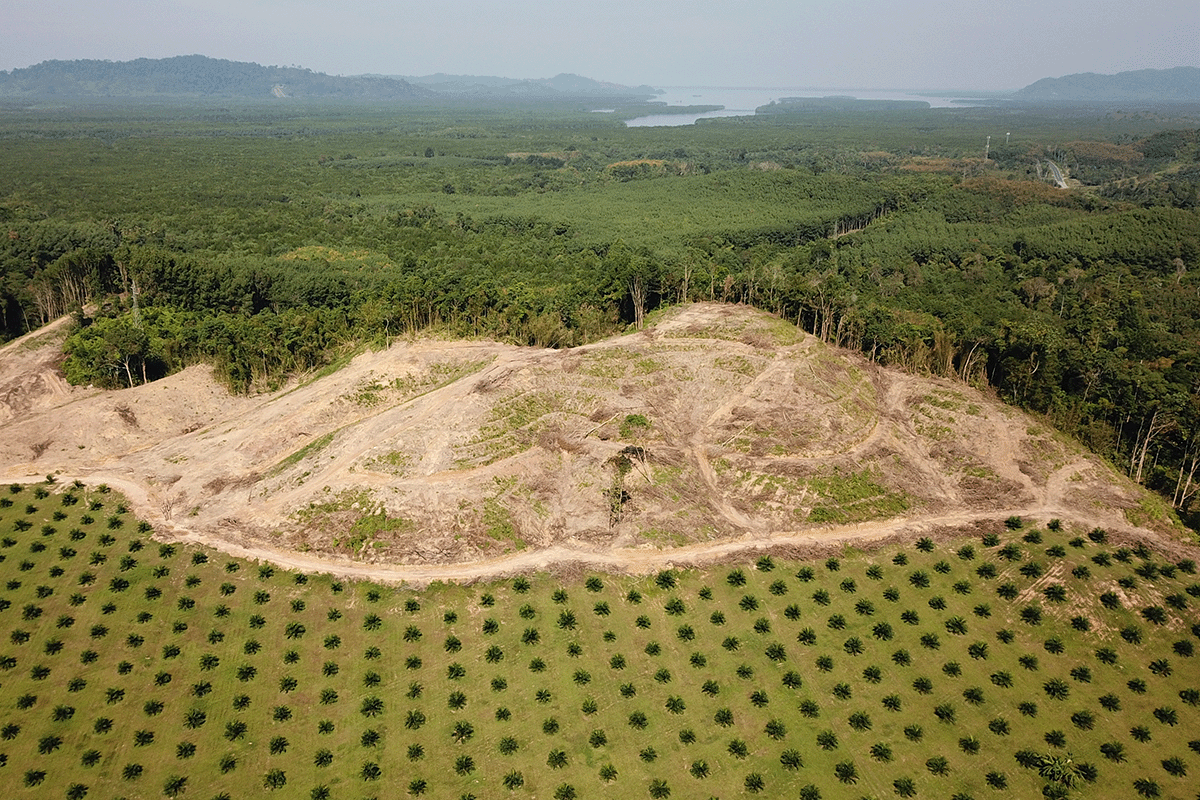 Signs of deforestation close to a palm oil plantation in Indonesia.
Signs of deforestation close to a palm oil plantation in Indonesia.
The effects of deforestation in Indonesia
The loss of forest cover in Indonesia significantly impacts the environment, biodiversity, and local communities. Deforestation leads to soil erosion, which reduces soil fertility, making it harder for crops to grow.
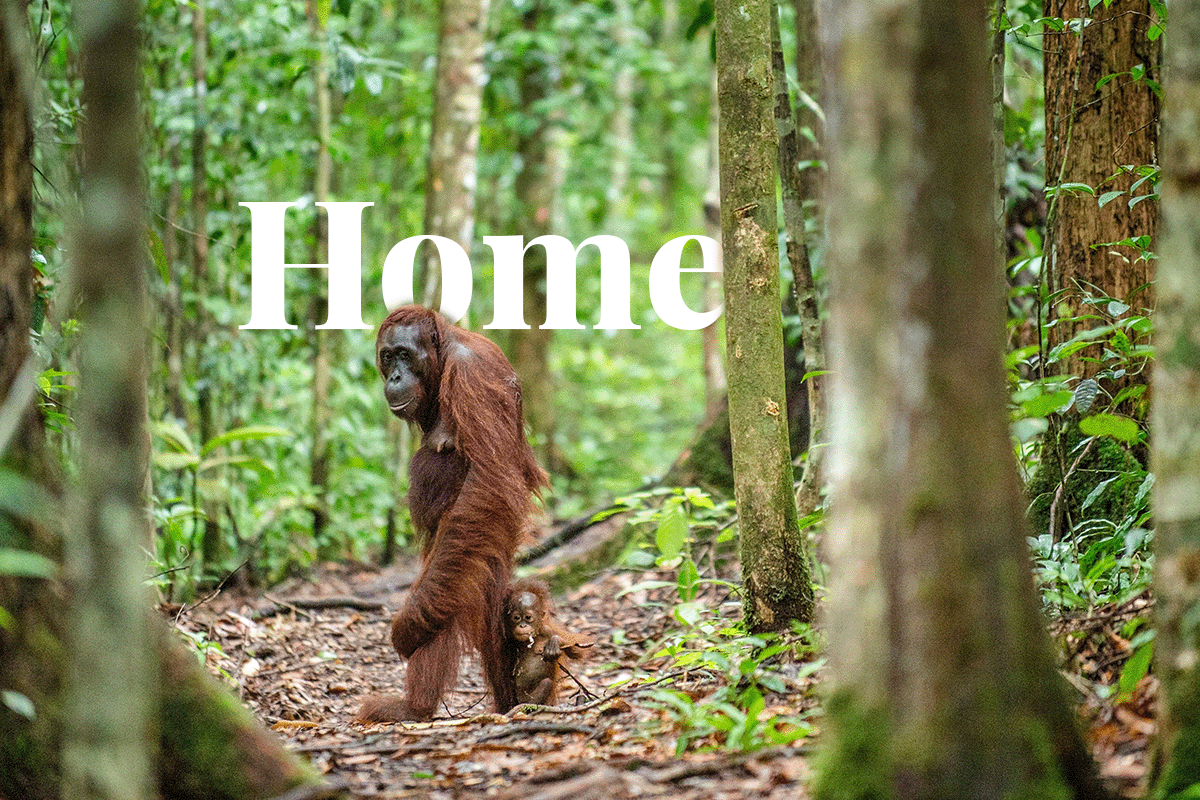
Indonesia's deforestation problem also affects its biodiversity. The country is home to many endangered species, such as orangutans, tigers, and elephants. The loss of forests and habitat destruction threatens these species' survival, and many have become critically endangered. The destruction of forests also affects the livelihoods of local communities that rely on forests for food, medicine, and income.
Read about: Countries with the highest deforestation rates in the world
Indonesia’s efforts to combat deforestation
Despite the challenges, Indonesia has made efforts to combat deforestation in recent years. The government introduced policies and regulations to protect forests and promote sustainable land use. For example, the moratorium on new permits for logging and palm oil plantations in primary forests and peatlands has been extended several times since 2011. The government has also launched programmes, such as the Social Forestry Programme, which allows communities to manage and protect forests, and the Forest and Landscape Restoration programme, which aims to restore degraded lands and forests.
Non-governmental organisations and the private sector have also played a crucial role in protecting Indonesia's forests. NGOs, such as the World Wildlife Fund and Conservation International, work with local communities to promote sustainable land use and support the development of sustainable livelihoods. The private sector, including companies in the palm oil industry, has committed to zero deforestation policies and sustainable sourcing of commodities.
However, despite these efforts, Indonesia's deforestation crisis is far from solved. Illegal logging and land clearing continue, and the government's efforts to enforce regulations and hold companies accountable have been insufficient. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a surge in deforestation as governments relaxed regulations to stimulate economic growth.
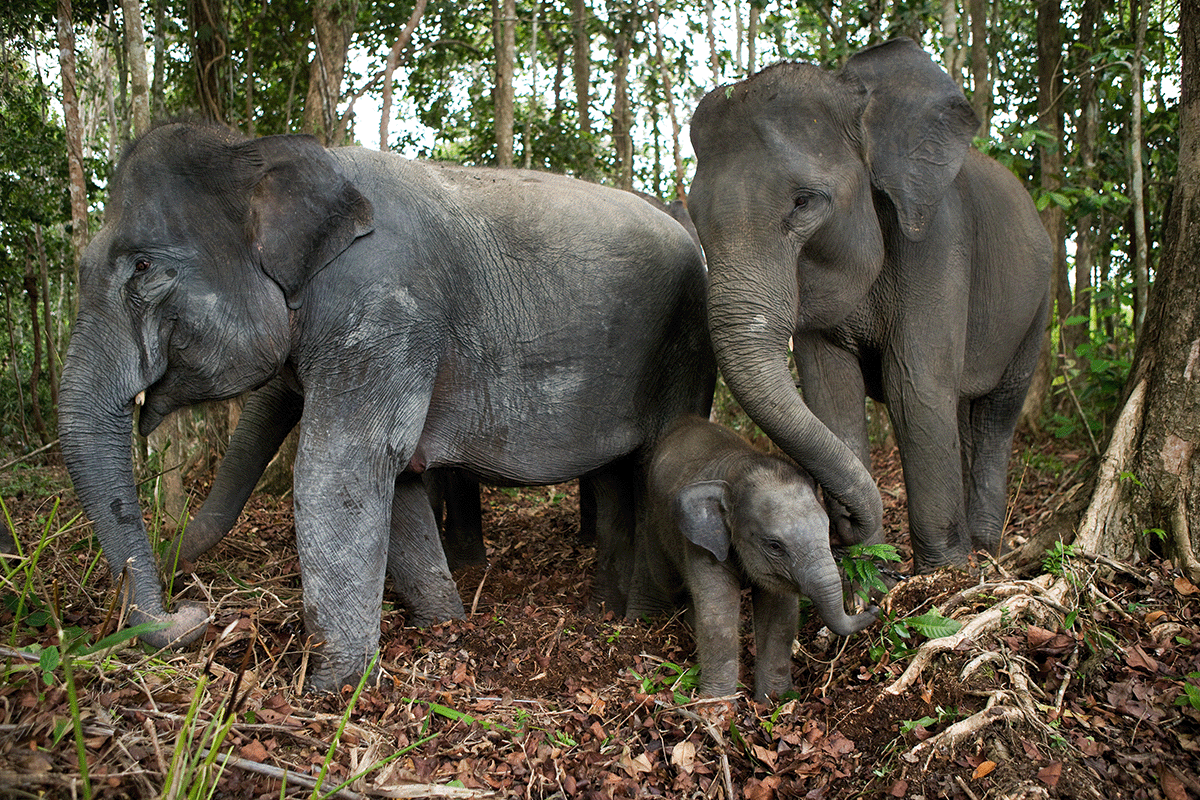 A family of Asian elephants in Sumatra, Indonesia.
A family of Asian elephants in Sumatra, Indonesia.
A firmer approach is needed
To address Indonesia's deforestation crisis, a comprehensive approach is needed that addresses the root causes of deforestation while promoting sustainable land use and community development. Strengthening law enforcement and holding companies accountable for illegal activities is essential. The government must also promote sustainable land use and alternative livelihoods for local communities. Finally, international cooperation and support are crucial to address the global demand for commodities that contribute to deforestation.
Read more: Deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest: causes, effects, solutions
Conclusion
In conclusion, Indonesia's deforestation problem has significant environmental, social, and economic implications. The expansion of agriculture and mining activities, illegal logging, and weak law enforcement are among the leading causes of deforestation in the country.
Although efforts have been made to address the issue, a comprehensive approach that promotes sustainable land use and community development is needed. This is what DGB Group aims to do, promote sustainable practices and reforest the world at scale. DGB works with various stakeholders, such as governments and communities, to develop large-scale impactful nature-based projects that restore nature and capture large amounts of carbon. These projects help the regeneration of biodiversity and the restoration of vital habitats.






