Welcome to the captivating realm of geographic information systems (GIS), where data analysis and geography intertwine to create a formidable tool. GIS seamlessly merges various forms of information, allowing us to visualise, analyse, and interpret geospatial data in ways previously unimaginable. This synergy of technology, geography, and data science has led to significant advancements in fields such as environmental conservation, resource management, and urban planning.
 Satellite picture of Inhaca Island.
Satellite picture of Inhaca Island.
In a world focused on environmental sustainability, the role of GIS cannot be overstated. It is an indispensable tool for monitoring and protecting our planet's natural ecosystems. By providing critical insights, GIS aids in preserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable practices.
The origins of GIS date back to the early 1960s with the development of computer-based mapping systems. Since then, GIS has evolved into a sophisticated system, serving as an essential resource for governments, scientists, businesses, and enthusiasts alike. Its evolution continues to shape our understanding of the world around us.
Understanding geographic information systems’ fundamentals
The pillars of GIS comprise hardware, software, and data. Hardware forms the backbone of the system, with robust processors and memory handling extensive datasets. Software acts as the orchestrator, providing a user-friendly interface for data manipulation and analysis. Meanwhile, data is the lifeblood of GIS, encompassing satellite imagery, aerial photography, LiDAR, and ground-based surveys.
How geographic information systems work: data collection, storage, analysis, and visualisation
The inner workings of GIS are both intricate and fascinating. Data collection involves sourcing information from various channels, including satellite sensors, GPS devices, and even social media. This treasure trove of data is meticulously stored, ready for intricate analyses and captivating visualisations. The power of GIS lies in its ability to unveil patterns within the data, presenting them through dynamic maps and 3D models.
Just as language fosters communication, GIS relies on standardised data formats to ensure seamless interactions between different systems. Formats like Shapefile, GeoJSON, and KML serve as the common tongue that translates spatial information across diverse platforms.
The power of geographic information systems
GIS technology is revolutionising the way we understand and manage our environment. Imagine a map that not only displays roads and landmarks but also offers real-time traffic updates, weather conditions, and points of interest. GIS brings this vision to life! GIS empowers various professionals to make informed decisions and ensure the preservation of our planet's delicate ecosystems.
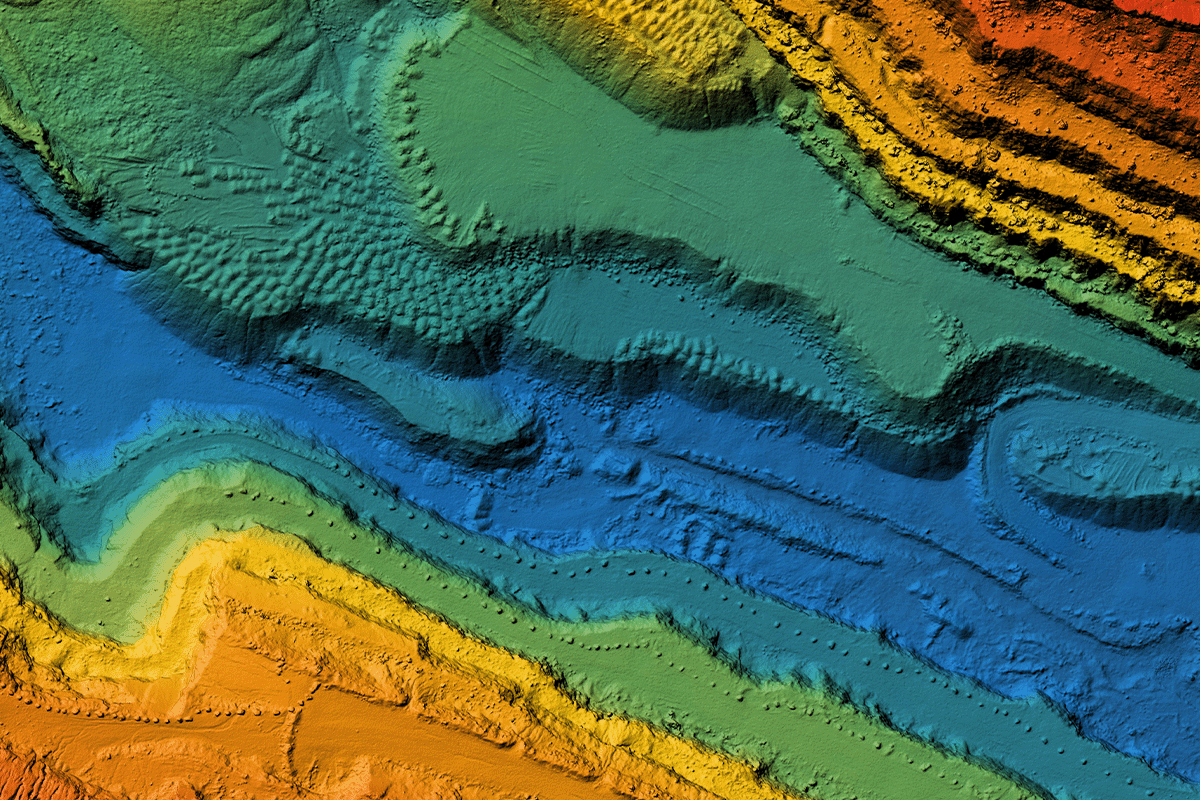 Digital elevation model. GIS product made after processing aerial pictures taken from a drone.
Digital elevation model. GIS product made after processing aerial pictures taken from a drone.
Diverse professions, one tool
- Surveyors, project developers, and cartographers: GIS serves as a powerful tool for professionals engaged in mapping, surveying, and developing projects, enabling them to create intricate maps with real-time data overlays.
- Conservationists and ecologists: For conservationists and ecologists, GIS provides essential information for habitat preservation, land-use planning, deforestation, and monitoring biodiversity. It aids in tracking wildlife populations and identifying areas vulnerable to climate change, contributing to the longevity of our natural resources.
- Resource managers: GIS plays a pivotal role in resource management, offering insights into natural hazards, risk assessment, and change detection. It enables effective planning and preparation to mitigate the impact of disasters.
- Urban planners: As cities evolve, urban planning becomes increasingly complex. GIS provides a blueprint for designing smart cities, optimising transportation networks, and ensuring equitable access to essential services.
Geographic information systems in natural resource management
- Hazard and risk assessment: GIS enables us to anticipate and mitigate natural disasters. It is instrumental in identifying and assessing natural hazards, such as floods, landslides, earthquakes, and forest fires. It aids in conducting risk assessments and estimating potential damage, assisting in early planning and preparedness.
- Change detection: GIS monitors environmental changes that impact natural resources, allowing for informed decision-making. It identifies areas vulnerable to change and helps develop strategies for protection.
- Analysis and modelling: GIS's analytical capabilities generate maps and charts that reveal trends, patterns, and environmental conditions. It aids in preparing, implementing, and monitoring management plans for specific regions.
- Environmental monitoring: GIS is employed to monitor the growth and decline of natural resources, tracking changes in land use, forest cover, and land conditions. It enables real-time monitoring of ecological factors like water bodies and pollution levels, as well as deforestation.
- Natural resource inventory: From forest management to watershed management, GIS assists in monitoring and managing natural resources. It maps subterranean mineral deposits and aids in assessing forest cover, identifying encroachments, and determining best land-use practices.
Read more: Net zero: benefits, challenges, strategies, and the power of nature-based solutions
The functionality of geographic information systems
- 3D modelling and visualisation: GIS extends beyond traditional maps to 3D modelling and visualisation, enhancing our understanding of landscapes and structures. It proves invaluable in city planning, architecture, and environmental assessments.
- Remote sensing integration: GIS seamlessly incorporates remote sensing data from satellites, drones, and aerial technologies. It aids in monitoring land cover changes, assessing crop health, and tracking global deforestation.
- Time-series data analysis: GIS enables the observation of landscapes evolving over time, identifying trends and patterns and predicting future developments—critical for resource management and future planning. Similar to a masterful analyst, GIS empowers businesses to query vast databases, retrieving precise information with a simple command, fostering informed decisions.
- Satellite imagery and LiDAR: Satellite imagery and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data form the cornerstone of GIS, offering a bird's-eye perspective of our planet. LiDAR, the analytical tool of GIS, uses lasers to measure distances and craft detailed elevation models. These visuals and technology are essential for environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster response, terrain analysis, flood modelling, and archaeological investigations.
- Spatial analysis: Akin to deciphering relationships between geographical elements, GIS encompasses overlaying data layers, creating buffers around specific points, and assessing feature proximity. These techniques underpin urban development, conservation initiatives, and emergency response strategies.
- Ground-based surveys: Ground-based surveys and field data collection enrich GIS databases with firsthand information, capturing insights from water quality measurement to wildlife behaviour tracking.
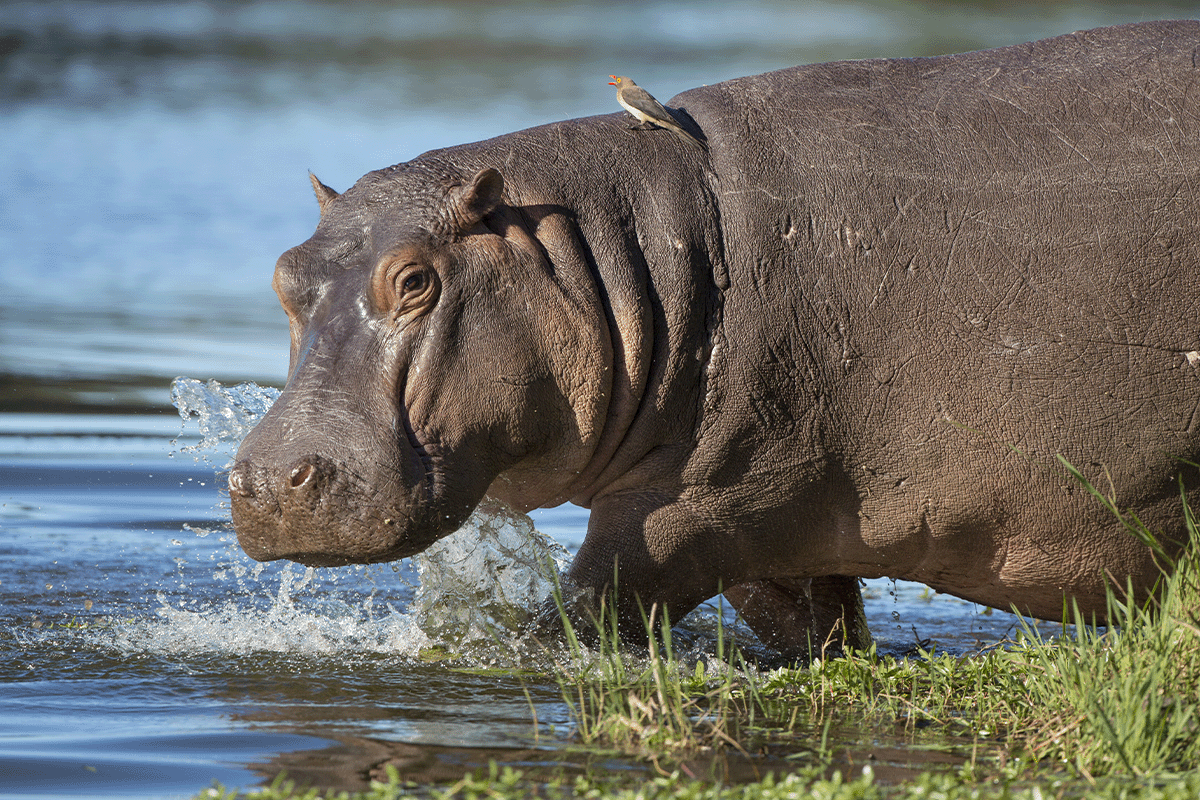 GIS databases can be key to wildlife behaviour tracking in their natural habitat.
GIS databases can be key to wildlife behaviour tracking in their natural habitat.
GIS emerges as a stalwart ally in the quest for sustainable resource management and to preserve our planet's delicate ecosystems. Its versatility and power enable professionals, industries, and governments to collaborate and make informed decisions, ensuring the preservation and effective utilisation of our planet's precious resources and minimising ecological consequences. This knowledge is paramount in ensuring the longevity of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Read more: 10 Vital ecosystem services: sustaining life on Earth
Geographic information systems’ practical applications
Environmental conservation
Environmental conservation is a noble pursuit that relies on meticulous observation and data-driven decision-making. Enter GIS, an invaluable tool for environmentalists and conservationists. In the world of biodiversity protection, GIS offers an array of applications. It enables the tracking of endangered species by analysing their habitats, migratory patterns, and interactions with their surroundings.
GIS also plays a crucial role in monitoring forest cover changes over time, aiding in the detection of deforestation and illegal logging activities. Identifying ecological corridors—the vital pathways that connect fragmented habitats—is another area where GIS shines. By merging real-time sensor and GPS data with GIS technology, conservationists gain a potent edge. This amalgamation enhances the accuracy of data collection and enables swift responses to emerging challenges, ensuring the preservation of our planet's natural wonders for generations to come.
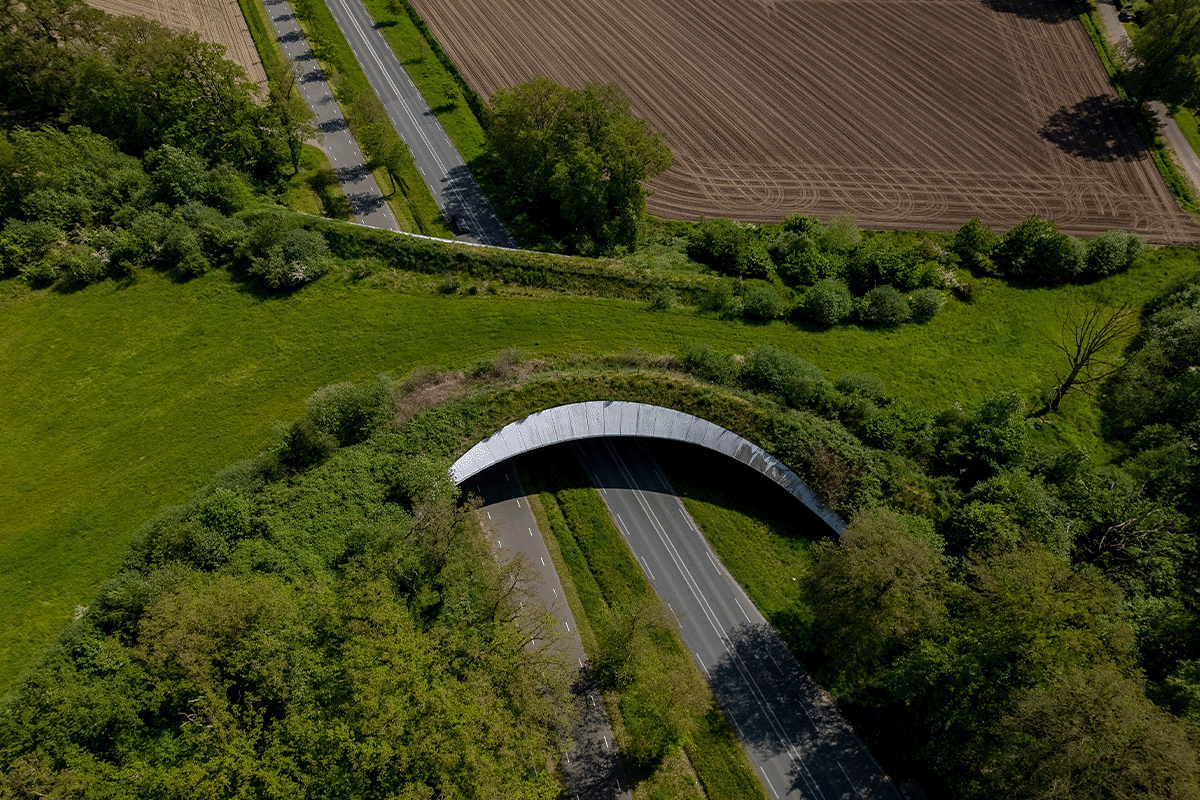 GIS excels in identifying ecological corridors, crucial pathways connecting fragmented habitats.
GIS excels in identifying ecological corridors, crucial pathways connecting fragmented habitats.
Geographic exploration for mineral resources
The pursuit of valuable minerals is a journey involving environmental and ethical considerations. Here, GIS emerges as a guiding beacon. It seamlessly merges geological data with the visual prowess of satellite imagery, creating a comprehensive picture of potential mineral resources. This integration aids in responsible mining practices that prioritise both resource extraction and ecological balance.
GIS identifies optimal locations for extraction, minimising impact on sensitive habitats and biodiversity-rich areas. By incorporating factors like terrain characteristics, land use patterns, and proximity to water bodies, GIS enables mining companies to make informed decisions that reduce environmental footprints. This, in turn, promotes sustainable mineral exploration while preserving the intricate balance of our planet's ecosystems.
Mapping geographic hazards and disaster management
Nature's unpredictable fury often reminds us of its enigmatic power. To tackle this uncertainty, GIS emerges as a formidable tool in hazard mapping and disaster management. By meticulously analysing geological data, historical records, and topographical features, GIS pinpoints regions vulnerable to natural disasters.
This proactive approach allows communities and governments to devise strategies for disaster mitigation and response. GIS-generated hazard maps identify flood-prone areas, earthquake zones, and potential landslide sites, acting as essential guides for urban planning and infrastructure development. By leveraging the insights provided by GIS, cities can bolster their resilience, saving lives and safeguarding communities from the unexpected upheavals of nature.
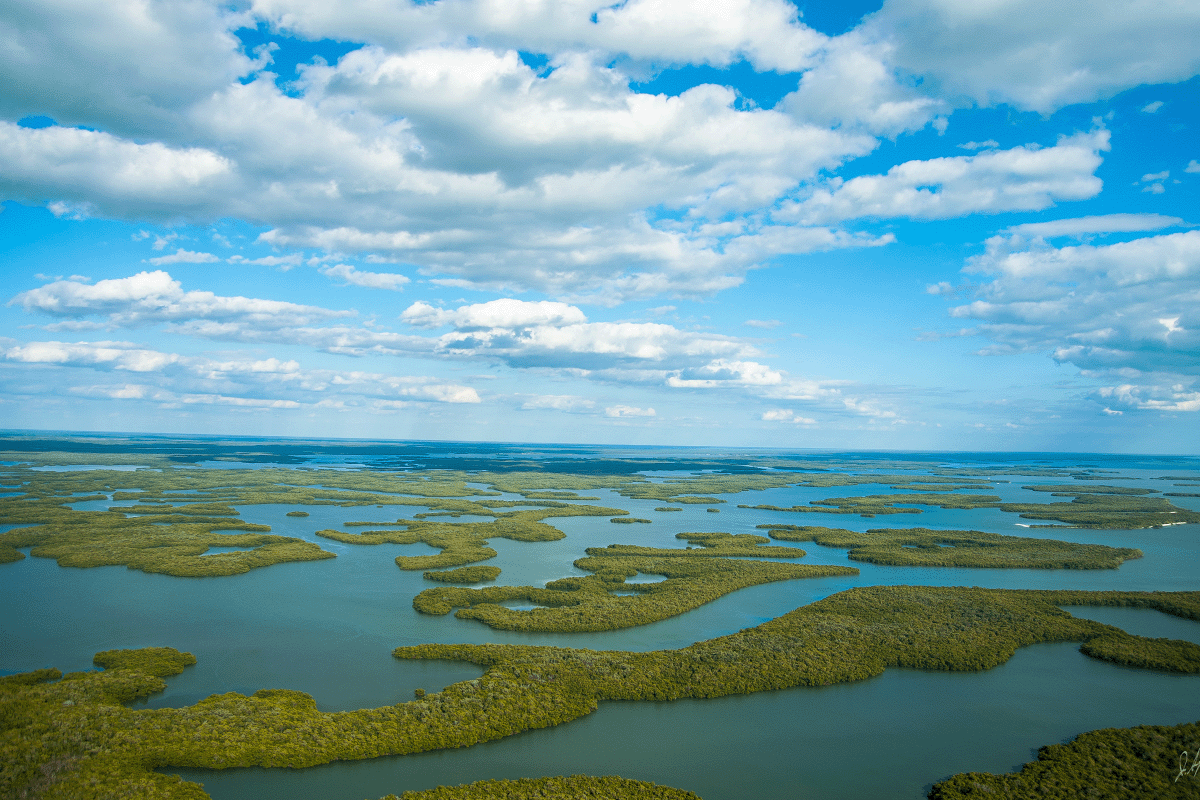 GIS is a powerful tool in addressing nature's unpredictability, precisely identifying disaster-prone areas through thorough analysis of geological data, historical records, and topography.
GIS is a powerful tool in addressing nature's unpredictability, precisely identifying disaster-prone areas through thorough analysis of geological data, historical records, and topography.
Challenges and limitations of geographic information systems
Every scholar recognises the importance of precise knowledge. Similarly, in GIS, data accuracy and reliability are fundamental. Errors in data collection or outdated information can mislead decisions and hinder progress.
As sophisticated as GIS is, it demands substantial computational power and time for processing and analysis. Technological advancements are essential to meet the escalating demands of GIS applications. Much like understanding diverse dialects, integrating data from different sources with varying formats and resolutions can prove intricate for GIS users. These challenges, however, are opportunities in disguise. They propel the refinement of GIS technology and broaden its accessibility.
Future trends in geographic information systems
The future promises exciting advances in GIS technology. Expect swifter processing, refined data collection methods, and enhanced integration of GIS with emerging technologies.
The fusion of GIS with AI and machine learning adds a new dimension. This synergy automates pattern recognition, trend prediction, and hidden data relationships, empowering decision-makers.
The utilisation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), or drones, in GIS will soar. These agile devices capture high-resolution imagery and collect data from remote areas, offering fresh perspectives.
As climate challenges unfold, GIS stands as a reliable tool in its mitigation. Analysing climate data, modelling scenarios, and identifying vulnerable regions, GIS supports policymakers in adapting to and combating climate change.
Read more: How are carbon credits issued?
DGB Group: innovating sustainability through disruptive technologies
In this enlightening exploration of geographic information systems (GIS), we've delved into how GIS revolutionises our perception and interaction with the world. It guides sustainable practices, aids urban planning, and empowers environmental decision-making, painting a clearer picture of a promising future.
As we tread this transformative path, let's embrace GIS's potential to inform choices and preserve our planet. Like scholars refining their skills, we, too, must persist in advancing our knowledge and methods through pioneering technology like GIS. As we move towards a circular, decarbonised economy, let's harness GIS's potential for a brighter, greener future.
Amid this era of innovation, DGB Group embodies the synergy between technology and environmental responsibility. Leveraging AI, blockchain, big data, and drone technology, DGB pioneers high-quality nature-based solutions, setting new standards for nature restoration and sustainability.
Join DGB in this transformative mission

 Satellite picture of Inhaca Island.
Satellite picture of Inhaca Island. Digital elevation model. GIS product made after processing aerial pictures taken from a drone.
Digital elevation model. GIS product made after processing aerial pictures taken from a drone.
 GIS excels in identifying ecological corridors, crucial pathways connecting fragmented habitats.
GIS excels in identifying ecological corridors, crucial pathways connecting fragmented habitats. GIS is a powerful tool in addressing nature's unpredictability, precisely identifying disaster-prone areas through thorough analysis of geological data, historical records, and topography.
GIS is a powerful tool in addressing nature's unpredictability, precisely identifying disaster-prone areas through thorough analysis of geological data, historical records, and topography.
